RIYADH: Introduced during Saudi Arabia’s G20 presidency, the Circular Carbon Economy Framework has gained significant traction, advancing emissions cuts, renewable energy investments, and carbon capture efforts.
In 2020, G20 leaders endorsed the framework to promote a sustainable, cost-effective approach to addressing climate change while ensuring clean energy access.
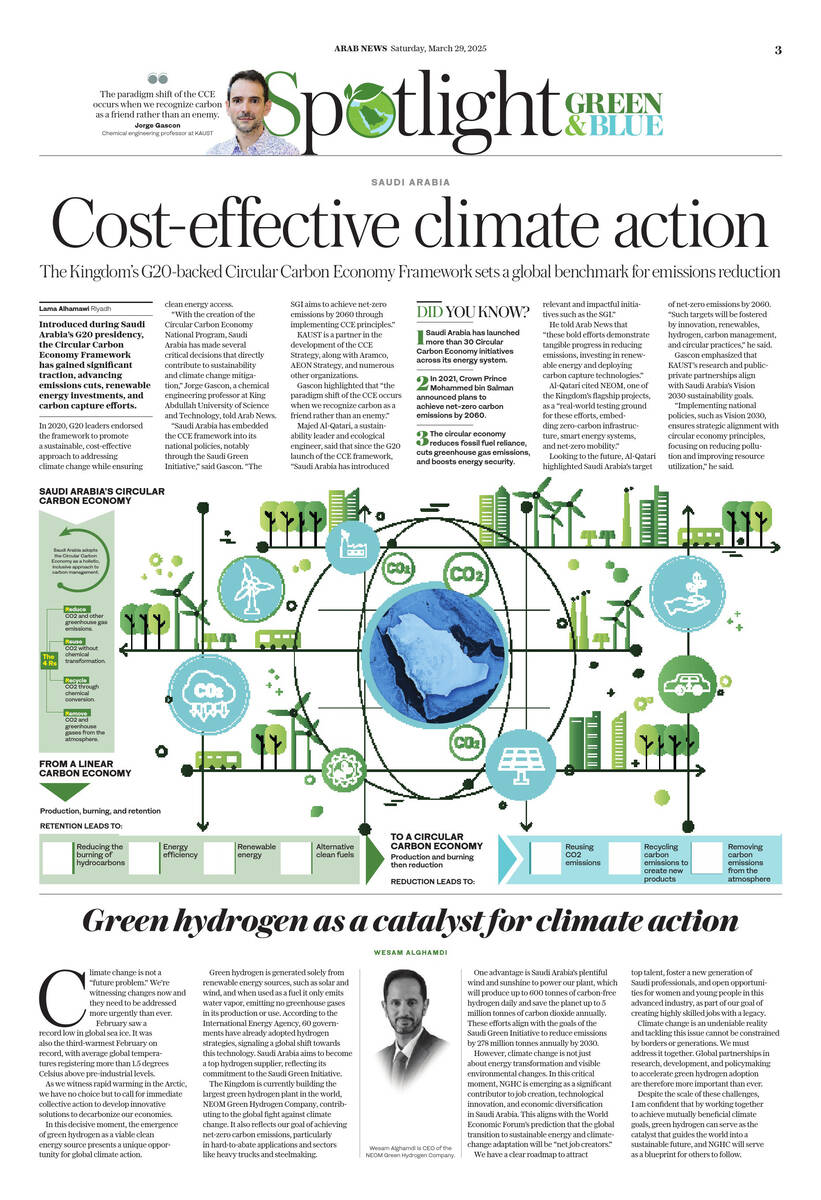
Building on this, the Kingdom launched its Circular Carbon Economy National Program in 2021 to reduce and offset carbon dioxide emissions through strategies of reduction, recycling, reuse, and removal.
“With the creation of the Circular Carbon Economy National Program, Saudi Arabia has made several critical decisions that directly contribute to sustainability and climate change mitigation,” Jorge Gascon, a chemical engineering professor at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, told Arab News.
These decisions include “policy integration, renewable energy investment, and carbon capture initiatives.”
The program also recognizes the importance of natural carbon absorption and sets an ambitious goal to sustainably manage, restore, and preserve 1 billion hectares of degraded land by 2040 using all available mitigation strategies.

Jorge Gascon
“Saudi Arabia has embedded the CCE framework into its national policies, notably through the Saudi Green Initiative,” said Gascon.
“The SGI aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2060 through implementing CCE principles and accelerating the transition to a green economy through emissions reduction, afforestation, and protection of land and sea.”
He noted that Saudi Arabia is shifting its energy mix toward sustainability, with a goal of 50 percent renewable energy.
DID YOU KNOW?
• Saudi Arabia has launched more than 30 Circular Carbon Economy initiatives across its energy system.
• In 2021, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman announced plans to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2060.
• The circular economy reduces fossil fuel reliance, cuts greenhouse gas emissions, and boosts energy security.
On carbon capture, Gascon said: “The Kingdom is engaged in international advocacy, notably during its G20 presidency and beyond, as well as various collaborative efforts and knowledge-sharing initiatives through institutions such as KAPSARC and KAUST.”
KAUST is a partner in the development of the CCE Strategy, along with Aramco, the King Abdullah Petroleum Studies and Research Center, AEON Strategy, and numerous other organizations.
The CCE’s development aligns with earlier efforts to promote sustainability. At the Future Investment Initiative forum in 2019, Saudi Energy Minister Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman discussed the CCE.
The following year, at the G20 Leaders’ Summit in Riyadh, King Salman introduced the National Program for the Circular Carbon Economy during the “Safeguarding the Planet” event, urging global cooperation to address climate change “by developing the economy and increasing human prosperity.”
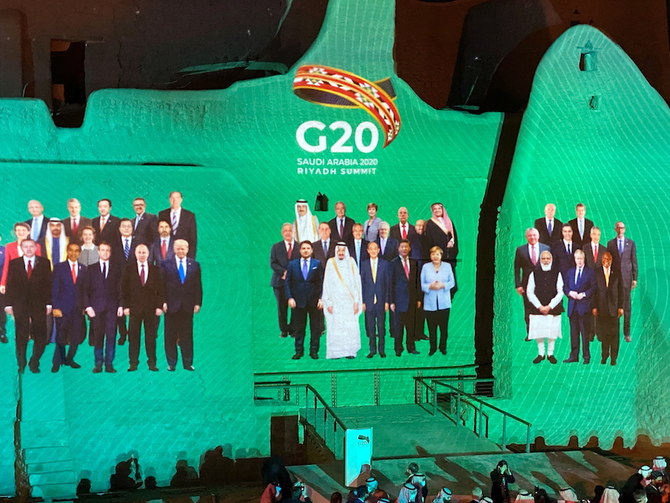

"Family Photo" for annual G20 Summit World Leaders is projected onto Salwa Palace in At-Turaif. (AN file)
Before the national program, Saudi Arabia had many initiatives focusing on carbon capture and conversion into valuable raw materials.
“Numerous areas of research at KAUST intersect with CCE, including catalysis, clean combustion, advanced membranes, and porous materials,” Gascon said. “KAUST supported a parallel Circular Carbon Initiative to capture the contributing science and technology.”
He added: “CCE builds on the principles of the circular economy while recognizing that removal must play a key role in achieving this circularity.
“In this way, a 4R (reduce, reuse, recycle, remove) approach is proposed to manage carbon emissions effectively, resulting in a closed loop that minimizes waste and CO2 emissions.”
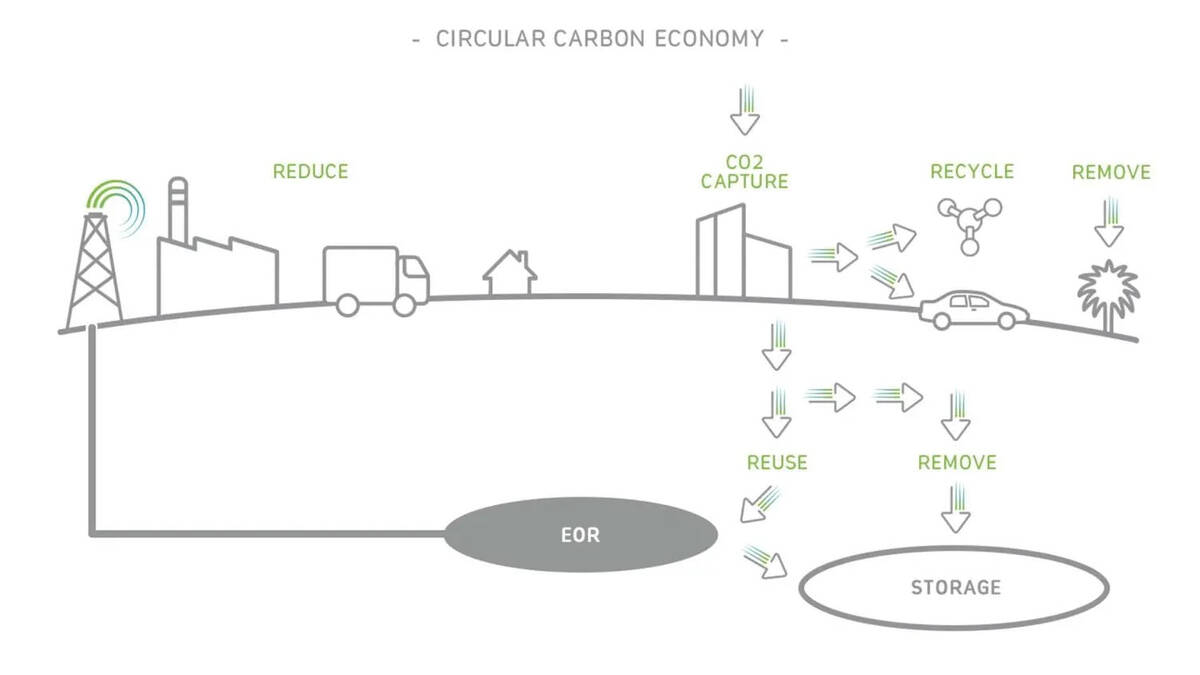
Illustration image courtesy of Aramco.com
Gascon highlighted that “the paradigm shift of the CCE occurs when we recognize carbon as a friend rather than an enemy.”
Through the Circular Carbon Economy Framework and various energy initiatives, Saudi Arabia is strategically establishing itself as a global leader in CCE.
This position is backed by the Kingdom’s abundant natural resources, significant technological investments and a strong commitment to sustainable development.
Majed Al-Qatari, a sustainability leader, ecological engineer, and UN youth ambassador, said that since the G20 launch of the CCE framework, “Saudi Arabia has introduced relevant and impactful initiatives such as the Saudi Green Initiative and the National Renewable Energy Program.”
He told Arab News that “these bold efforts demonstrate tangible progress in reducing emissions, investing in renewable energy and deploying carbon capture technologies.”
Al-Qatari cited NEOM, one of the Kingdom’s flagship projects, as a “real-world testing ground for these efforts, embedding zero-carbon infrastructure, smart energy systems, and net-zero mobility.”

Ecological engineer and UN youth ambassador Majed Al-Qatari. (AN file)
He added: “In 2025 and beyond, I expect further scaling of blue and green hydrogen projects, along with enhanced regional cooperation in carbon management.”
Al-Qatari also highlighted the four pillars of the CCE framework: reduce, reuse, recycle, and remove.
“The Kingdom applies this through initiatives like energy efficiency standards (reduce), CO2 utilization in industrial processes (reuse), circular water reuse in agriculture (recycle), and large-scale carbon capture and storage projects such as those by Aramco/SABIC (remove),” he said.
Asked what he believes was the motivating factor for Saudi Arabia’s adoption of the Circular Carbon Economy Framework during the G20, Al-Qatari said: “Saudi Arabia sought to play a leading role in advancing a global dialogue that aligns climate goals with economic mandates.
“The CCE framework was introduced in order to showcase an inclusive, technologically neutral mechanism that takes into account relevant pathways to mitigate carbon emissions without compromising energy security or economic development.”
Al-Qatari noted that the framework has become a global reference model, particularly for hydrocarbon-reliant economies.
“The framework offers a transition pathway that is practical and inclusive of conventional sources of energy like oil and gas while advancing climate goals,” he said. “Other jurisdictions are considering the Kingdom’s model in order to customize it for their local contexts.”

Saudi Green Initiative illustration
Looking to the future, Al-Qatari highlighted Saudi Arabia’s target of net-zero emissions by 2060. “Such targets will be fostered by innovation, renewables, hydrogen, carbon management, and circular practices,” he said.
“Future goals would involve expanding circularity practices into other sectors and materials such as water, and waste sectors, while also crystallizing local environmental, social, and governance markets and strengthening regulatory frameworks for corporate sustainability and sustainable finance.”
When asked about the role of innovation and technology in advancing CCE, Gascon stressed KAUST’s importance in research and development.
“KAUST is pioneering breakthroughs in CO2 capture, including direct air capture, cryogenic CO2 capture, and other point-source technologies, as well as nature-based carbon sequestration strategies and geological storage solutions,” he said.
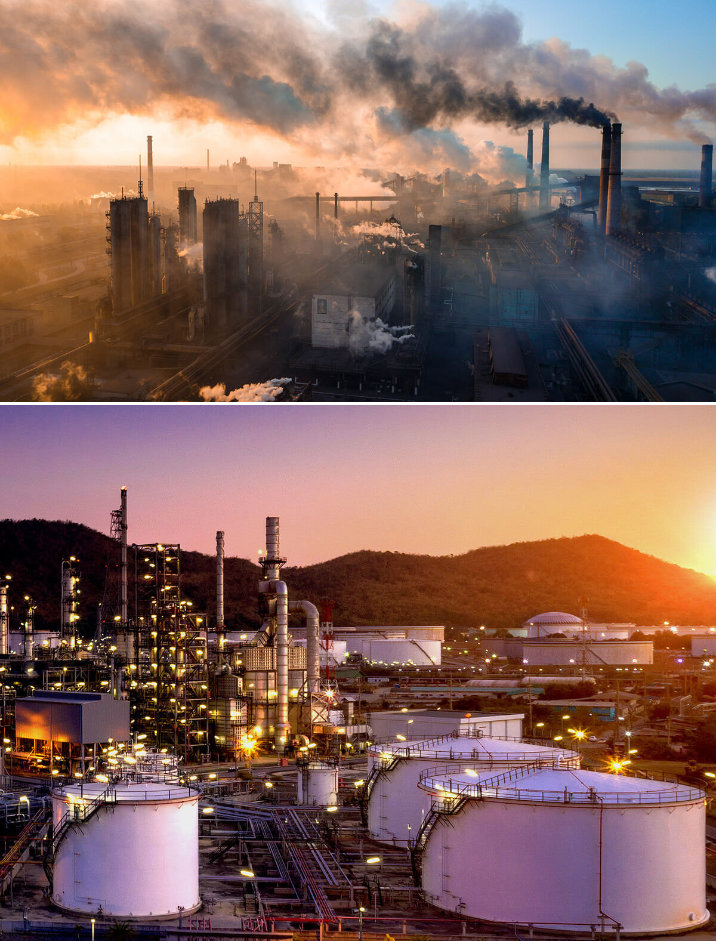

KAUST is pioneering breakthroughs in CO2 capture, including direct air capture, cryogenic CO2 capture, and other point-source technologies. (KAUST photos)
“It also drives advancements in synthetic fuels, such as clean ammonia and hydrogen carriers, alongside the integration of renewable energy and the optimization of industrial processes.
“KAUST collaborates with industry leaders, including Saudi Aramco and NEOM, to accelerate the deployment of carbon capture and sustainable fuel technologies.”
Gascon emphasized that KAUST’s research and public-private partnerships align with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 sustainability goals.
“Implementing national policies, such as Vision 2030, ensures strategic alignment with circular economy principles, focusing on reducing pollution and improving resource utilization,” he said.